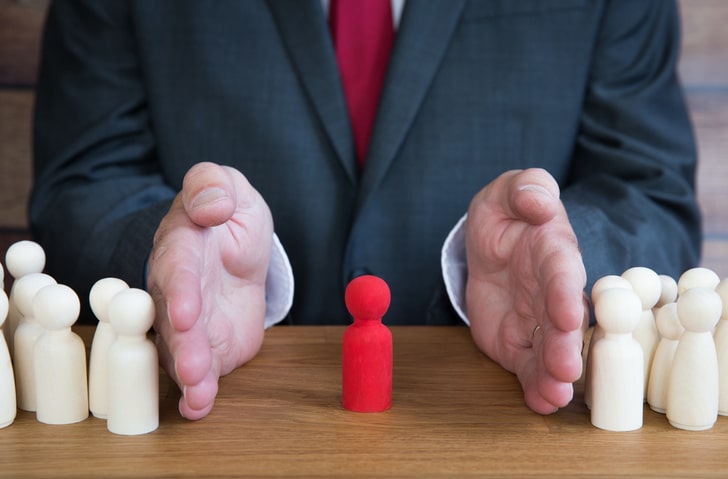
Los Angeles Employment Discrimination Lawyers
Both California and federal laws prohibit discrimination in the workplace. Discrimination generally means unequal or unfair treatment based on certain personal characteristics. Unlawful discrimination occurs when an employer fires, demotes, refuses to hire, or otherwise treats an employee unfairly because of his or her medical condition, age, sex, race, or other characteristics protected by law.
The Los Angeles employment discrimination attorneys at Broslavsky & Weinman, LLP represent employees who have suffered unlawful discrimination on the job. Victims of discrimination can seek compensation for lost pay and benefits, emotional pain and suffering, and other potential damages.
Our Los Angeles employment attorneys are experienced in investigating, negotiating, and successfully litigating employment discrimination claims and have helped numerous employees across all types of industries achieve favorable outcomes and obtain compensation for their injuries.

Types of Unlawful Discrimination:
There are many personal characteristics protected under the law. Some of the most common kinds of claims handled by our Los Angeles discrimination attorneys include but are not limited to:
Disability Discrimination. It is illegal to discriminate against a worker because of his or her physical or mental disability. Disabilities can be either short-term or long-term. Employers must provide reasonable accommodation to employees with disabilities, and must engage in good faith discussions with the employees to determine what accommodations are needed.
Age Discrimination. It is illegal for an employer to discriminate against employees based on age. Employees over 40 years old are protected from being treated differently or being forced out of work as a result of their age.
Gender and Pregnancy Discrimination. Employers are prohibited from treating employees differently because of their gender, as well as discriminating against employees due to pregnancy or medical conditions related to pregnancy or childbirth.
Race and National Origin Discrimination. It is unlawful for an employer to discriminate against employees because of their race, color, ancestry or national origin.
Other personal characteristics protected under the law against discrimination include religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, marital status, and genetic information.
What Conduct Qualifies as Discrimination?
To successfully bring a claim for job discrimination, an employee has to show that the employer took negative employment action against him or her and that the negative employment action was at least in part motivated by discrimination. Negative employment actions can include:
- Termination or firing
- Being forced to quit
- Demotion
- Unfavorable transfer or job assignment
- A decrease in pay or reduction of benefits
- Denial of promotion or advancement
- Failure to hire
- Any other negative decision that significantly affects the terms and conditions of employment
At Broslavsky & Weinman, LLP, we also offers the following services:
- Wrongful Termination
- Sexual Harassment
- Family and Medical Leave
- Wage & Hour Violations
- Breach of Contract & Fraud
- Whistleblower
- Age Discrimination
- Disability Discrimination
- Race Discrimination
- Gender & Pregnancy Discrimination
How Are Discrimination Cases Proven?
An employee does not need to prove that discrimination was the only motivating factor. Termination or other negative employment action may still be considered wrongful under the law if it is based on a mix of both legal and illegal reasons.
Naturally, employers are unlikely to admit that they had any illegal reasons and that a discriminatory motive played any role in the negative employment action. Two types of evidence can be used to prove discrimination – direct and indirect. Direct evidence typically consists of discriminatory statements by the employer or supervisor.
Indirect evidence can come in many forms. Effective indirect evidence includes a showing that the employer’s stated reason for the negative employment action is untrue or makes no sense. For example, if an employer claims that the employee was terminated because there is not enough work but hired other employees shortly before the termination, the employee will have a good argument that discrimination must have played a role and termination was unlawful.
Another effective type of indirect evidence is showing that there is a pattern of unfair treatment at work and that other co-workers with the same protected characteristics experienced negative treatment.
Contact Los Angeles Employment Discrimination Attorneys for Free Case Consultation
If you believe you have experienced unlawful discrimination at your work, contact our Los Angeles employment discrimination attorneys to assist you. You can call us at (310) 575-2550 or email us using the contact form on this page for a free consultation and to find out more about your rights and potential claims.
With office locations in Los Angeles and San Bernardino, our employment lawyers provide legal services and representation to clients throughout California.
Related Links:
- Study Finds 1 in 4 Victims of Workplace Discrimination Face Stress and Depression
- Female and Underrepresented Minority Workers in California Restaurants Often Experience Discrimination, Study Finds
- Global Security and Aerospace Firm Named in New Employment Discrimination Lawsuit
- Home Improvement Company Settles Disability Discrimination Case for $8.6 Million
- Groundbreaking EEOC Ruling Protects LGBT Workers from Sexual Orientation Discrimination
Frequently Asked Questions for our Los Angeles Employment Discrimination Lawyer
What is employment discrimination?
Employment discrimination is the unjust treatment of employees or job applicants based on their protected characteristics, such as race, gender, age, religion, or disability. This type of discrimination can occur during any aspect of the employment relationship, including hiring, promotion, compensation, job training, termination, or any other term or condition of employment.
What are the protected characteristics under employment discrimination laws?
The protected characteristics under employment discrimination laws include race, color, national origin, sex, pregnancy, age, religion, disability, and genetic information. In some states, additional protected characteristics, such as sexual orientation or gender identity, are also recognized.
What is the difference between harassment and discrimination?
Harassment is a form of employment discrimination that involves unwanted behavior, such as teasing, jokes, or comments, based on a protected characteristic. Discrimination, on the other hand, involves treating employees or job applicants unfairly based on a protected characteristic. For example, failing to promote a qualified employee because of their race would be considered discrimination, while making racial slurs to that employee would be considered harassment.
Who is protected under employment discrimination laws?
Employment discrimination laws protect all employees, regardless of their race, gender, age, religion, or disability. Job applicants are also protected under these laws, as they cannot be treated unfairly during the hiring process based on protected characteristics.
What should I do if I believe I have been the victim of employment discrimination?
If you believe you have been the victim of employment discrimination, you should immediately report the incident to your employer and document any evidence, such as emails, notes, or witness statements. You may also want to consider filing a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) or a similar state agency. An experienced employment discrimination lawyer can help you navigate the complaint process and advocate on your behalf.
Can I file a complaint if I am still employed?
Yes, you can file a complaint if you are still employed. However, some employers may choose to retaliate against employees who file complaints, so it is important to have the support of an experienced employment discrimination lawyer.
What happens after I file a complaint with the EEOC?
After you file a complaint with the EEOC, the agency will conduct an investigation into your allegations. If the EEOC determines that there is sufficient evidence to support your complaint, it may attempt to mediate a settlement between you and your employer. If a settlement cannot be reached, the EEOC may choose to bring a lawsuit on your behalf.
What kind of damages can I recover if I win my employment discrimination case?
If you win your employment discrimination case, you may be able to recover a wide range of damages, including back pay, front pay, lost benefits, and emotional distress damages. In some cases, you may also be able to recover attorney’s fees and other costs associated with your case.